-
GlOMERULAR DISEASE
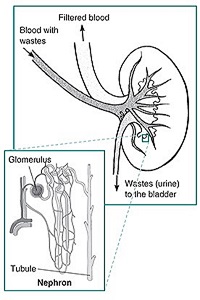
A glomerulus is a network (as a tuft) of capillaries located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney. It serves as the first stage in the filtering and cleaning process of the blood carried out by the nephron in its formation of urine.
Many conditions affect kidney function by attacking the the tiny units of glomeruli. Glomerular diseases include many conditions with a variety of genetic and environmental causes and have the potential to lead to kidney failure. It refers to a group of symptoms including Edema, Proteinuria, Hyperlipidaemia,and Hypoalbuminemia.
It damages the glomeruli, letting protein and sometimes red blood cells leak into the urine. Sometimes a glomerular disease also interferes with the clearance of waste products by the kidney, so they begin to build up in the blood. Furthermore, loss of blood proteins like albumin in the urine can result in a fall in their level in the bloodstream. In normal blood, albumin acts like a sponge, drawing extra fluid from the body into the bloodstream, where it remains until the kidneys remove it. But when albumin leaks into the urine, the blood loses its capacity to absorb extra fluid from the body. Fluid can accumulate outside the circulatory system in the face, hands, feet, or ankles and cause swelling.
A number of different disease processes can damage the glomeruli and thereby cause kidney failure. Glomerulonephritis and glomerulosclerosis are broad terms that include many forms of damage to the glomeruli:
- Glomerulonephritis describes the inflammation of the membrane tissue in the kidney that serves as a filter, separating wastes and extra fluid from the blood.
- Glomerulosclerosis describes the scarring or hardening of the tiny blood vessels within the kidney.
Although glomerulonephritis and glomerulosclerosis have different causes, they can both lead to kidney failure. Some forms of kidney failure can be slowed down, but scarred glomeruli can never be repaired. Treatment for the early stages of kidney failure depends on the disease causing the damage.Early signs of kidney failure include blood or protein in the urine and swelling in the hands, feet, abdomen, or face. Kidney failure may be silent for many years.
SYMPTOMS:
albuminuria : large amounts of protein in the urine.
hematuria : blood in the urine.
reduced glomerular filtration rate : inefficient filtering of wastes from the blood.
hypoproteinemia : low blood protein.
edema : swelling in parts of the body
CAUSES:
A number of different diseases can result in glomerular disease. It may be the direct result of an infection or a drug toxic to the kidneys, or it may result from a disease that affects the entire body, like diabetes or lupus. Many different kinds of diseases can cause swelling or scarring of the nephron or glomerulus. Sometimes glomerular disease is idiopathic, meaning that it occurs without an apparent associated disease. The diseases described below can belong to two or more categories; manifesting primary and secondary causes: Diagnosing the pattern of Glomerular Disases is important because the outcome and treatment differs in different types. Primary causes are ones which are intrinsic to the kidney, whilst secondary causes are associated with certain infections (bacterial, viral or parasitic pathogens), drugs, systemic disorders (SLE, vasculitis) or diabetes.
A. Autoimmune Diseases
due to chronic underlying conditions, immune system of our body become invader against our own kidney instead of defending it and combating with the microbes and antigens. The immune system creates autoantibodies, which are antibodies or immunoglobulins that attack the body itself. Autoimmune diseases may be systemic and affect many parts of the body, or they may affect only specific organs or regions.
1. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) affects many parts of the body: primarily the skin and joints, but also the kidneys. . Lupus nephritis is the name given to the kidney disease caused by SLE, and it occurs when autoantibodies form or are deposited in the glomeruli, causing inflammation. The inflammation caused due to SLE and viral infection, may create scars that keep the kidneys from functioning properly.
2. Goodpasture's Syndrome: Goodpasture's Syndrome is a rare condition involing producing an autoantibody that specifically targets the kindey and lungs and it affects mostly young men but also occurs in women, children, and older adults. Its fitst indication is coughing up with blood and it causes progressive damage to the kidneys. Treatments include immunosuppressive drugs and a blood-cleaning therapy called plasmapheresis that removes the autoantibodies.
3. IgA nephropathy It is a form of glomerular disease that results when immunoglobulin A (IgA) forms deposits in the glomeruli, where it creates inflammation. The most common symptom of IgA nephropathy is blood in the urine, but it is often a silent disease that may go undetected for many years. This disease is estimated to be the most common cause of primary glomerulonephritis—that is, glomerular disease not caused by a systemic disease like lupus or diabetes mellitus. It appears to affect men more than women. Although IgA nephropathy is found in all age groups, young people rarely display signs of kidney failure because the disease usually takes several years to progress to the stage where it causes detectable complications.
B. Hereditary :
Nephritis—Alport SyndromeThe primary indicator of Alport syndrome is a family history of chronic glomerular disease, although it may also involve hearing or vision impairment. This syndrome affects both men and women, but men are more likely to experience chronic kidney disease and sensory loss.. Usually men can pass the disease only to their daughters. Women can transmit the disease to either their sons or their daughters. Treatment focuses on controlling blood pressure to maintain kidney function.
C. Infection-related Glomerular Disease:
Glomerular disease sometimes develops rapidly after an infection in other parts of the body.
1. Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN) can occur after an episode of strep throat or, in rare cases, impetigo (a skin infection). The Streptococcus bacteria do not attack the kidney directly, but an infection may stimulate the immune system to overproduce antibodies, which are circulated in the blood and finally deposited in the glomeruli, causing damage. PSGN can bring on sudden symptoms of swelling (edema), reduced urine output (oliguria), and blood in the urine (hematuria). Tests will show large amounts of protein in the urine and elevated levels of creatinine and urea nitrogen in the blood, thus indicating reduced kidney function. High blood pressure frequently accompanies reduced kidney function in this disease.
2. Bacterial endocarditis infection of the tissues inside the heart, is also associated with subsequent glomerular disease. Researchers are not sure whether the renal lesions that form after a heart infection are caused entirely by the immune response or whether some other disease mechanism contributes to kidney damage. Treating the heart infection is the most effective way of minimizing kidney damage. Endocarditis sometimes produces chronic kidney disease (CKD).
3. HIV the virus that leads to AIDS, can also cause glomerular disease. Between 5 and 10 percent of people with HIV experience kidney failure, even before developing full-blown AIDS. HIV-associated nephropathy usually begins with heavy proteinuria and progresses rapidly (within a year of detection) to total kidney failure.
D. Sclerotic Diseases
1. Glomerulosclerosis is scarring (sclerosis) of the glomeruli. In several sclerotic conditions, a systemic disease like lupus or diabetes is responsible. Glomerulosclerosis is caused by the activation of glomerular cells to produce scar material. This may be stimulated by molecules called growth factors, which may be made by glomerular cells themselves or may be brought to the glomerulus by the circulating blood that enters the glomerular filter.
2. Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of glomerular disease and of total kidney failure. Kidney disease is one of several problems caused by elevated levels of blood glucose, the central feature of diabetes. In addition to scarring the kidney, elevated glucose levels appear to increase the speed of blood flow into the kidney, putting a strain on the filtering glomeruli and raising blood pressure. Diabetic nephropathy usually takes many years to develop
3. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) describes scarring in scattered regions of the kidney, typically limited to one part of the glomerulus and to a minority of glomeruli in the affected region. FSGS may result from a systemic disorder or it may develop as an idiopathic kidney disease, without a known cause. Proteinuria is the most common symptom of FSGS,
E. Other Glomerular Diseases
1. Membranous nephropathy also called membranous glomerulopathy, is common cause of the nephrotic syndrome (proteinuria, edema, high cholesterol) after diabetic nephropathy. Diagnosis of membranous nephropathy requires a kidney biopsy, which reveals unusual deposits of immunoglobulin G and complement C3, substances created by the body's immune system. Fully 75 percent of cases are idiopathic, which means that the cause of the disease is unknown. The remaining 25 percent of cases are the result of other diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus, hepatitis B or C infection, or some forms of cancer.
2. Minimal change disease (MCD) is the diagnosis given when a patient has the nephrotic syndrome and the kidney biopsy reveals little or no change to the structure of glomeruli or surrounding tissues when examined by a light microscope. Tiny drops of a fatty substance called a lipid may be present, but no scarring has taken place within the kidney. MCD may occur at any age, but it is most common in childhood
AYURVEDIC TREATMENT
In Allopathy, proper cause as well as cure of the disease is not known and the line of treatment is the administration of various kinds of corticosteroids which temporarily decrease the excretion of protein in the urine and hold for a while, further complications associated with it. Immunosuppressive drugs are given to stop proteinuria in some patients, but once the treatments have ended proteinuria will continue. The drugs may sometimes damage the patient’s kidneys even more. Whereas in Ayurveda, we dig at the cause of the disease to treat the underlying cause and not just try to suppress the symptoms. Patients can have a remission after a period of steroid therapy. However, frequent relapse is a typical sign of Nephrotic Syndrome. So, there is no long term sustainable results and cure of Nephrotic Syndrome available in Allopathy.
Ayurveda believes that this condition is caused due to the vitiation of Pitta dosha in the body and various Pitta normalizing medications are used in the treatment of the sameAyurvedic treatment is a traditional treatment in India and works on the principle of targeting the cause and not symptoms, taking into consideration the prakriti and dosha equilibrium of the patient.
FACILITATION OF SERVICES:
In this today’s era of e-services, patients can avail free counselling from us through telephone or online query for all kinds of chronic and acute ailments and medicines are delivered at the doorstep of the patients in complete privacy. Our expert doctors’ in-depth knowledge, experience and four-tier evaluation and counselling criteria, enables patients to have customized treatment besides saving time in critical medical conditions. Personalized diet and post treatment follow up is taken regularly by our Technical Exerts to monitor the progress of patients. However, if it is convenient for patients, they can visit any of Information Centers after taking prior appointment. We also have full-fledged team of doctors and arrangements at Amritsar OPD to cater to the rush of patients.
For free consultation for a patient with glomerulonephritis please mail us with the scanned copy of reports by Click here